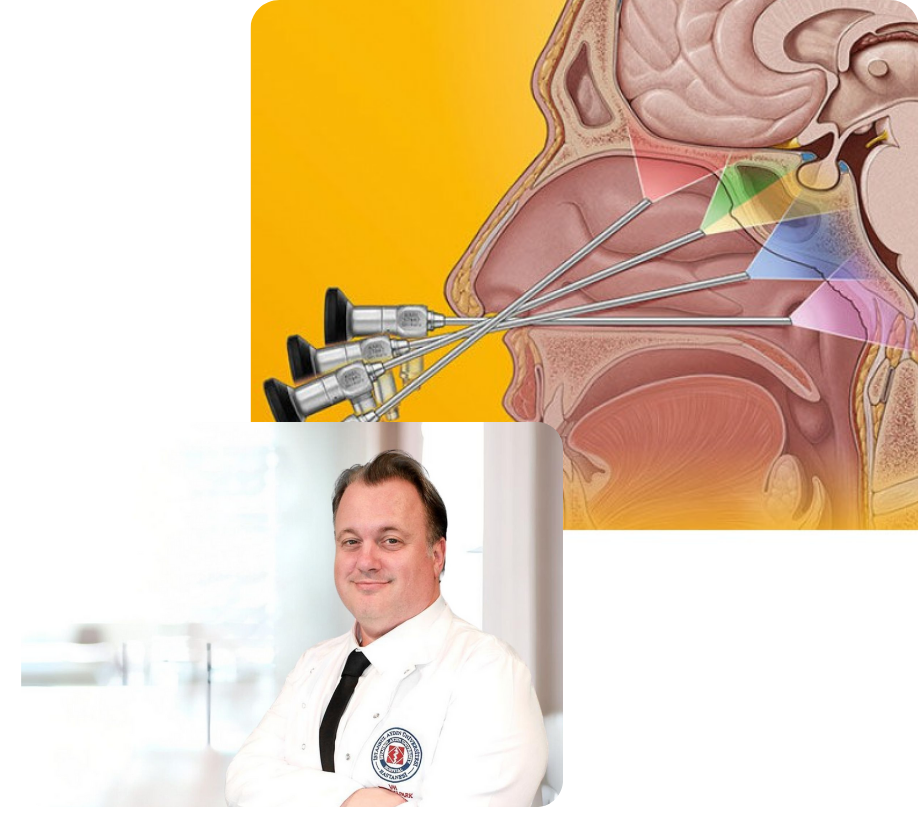
How Is Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery Performed?
Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is a minimally invasive technique that allows access to the pituitary gland through the nasal cavity. The surgeon uses a thin, illuminated tube called an endoscope to reach the pituitary gland via the sphenoid sinus. The camera at the tip of the endoscope provides the surgeon with high-resolution images, enabling them to visualize the tumor's location and size clearly. This allows for precise tumor removal.
- 1. Anesthesia and Preparation: The patient is placed under general anesthesia. During the surgery, the surgeon makes a small incision in the nasal cavity to insert the endoscope.
- 2. Insertion of the Endoscope: The endoscope is passed through the nasal cavity and positioned in the sphenoid sinus. At this stage, a small opening is made in the wall of the sphenoid sinus to access the pituitary gland.
- 3. Removal of the Tumor: Using the endoscopic visualization, the surgeon reaches the tumor and removes it with specialized surgical instruments. Once the tumor is removed, the pituitary gland and surrounding tissues are carefully examined.
- 4. Completion of the Procedure: After removing the tumor, the opening and nasal cavity are cleaned. Once the procedure is complete, the endoscope is removed, and the incision site is closed. The surgery typically takes 2-3 hours.
What Are the Advantages of Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery?
This surgical method offers several advantages compared to traditional open surgery:
- Minimally Invasive Approach: This surgery is performed with small incisions, resulting in minimal tissue damage and faster recovery for the patient.
- Reduced Pain and Faster Recovery: Postoperative pain is typically less severe, and patients can return to their normal activities more quickly.
- Improved Visualization: Endoscopic surgery provides the surgeon with a detailed view of the pituitary gland, enabling precise removal of the tumor.
- No Visible Surgical Scars: Since the surgery is performed through the nasal cavity, there are no visible scars on the skin.
- Fewer Complications: This method exerts less pressure on brain tissue and nerves, reducing the risk of complications.
Who Is Suitable for Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery?
Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is a suitable treatment option for patients with pituitary tumors and other pituitary gland disorders. However, the decision to perform surgery should be based on the patient’s condition, tumor size, location, and overall health.
- Pituitary Adenomas: This surgical method is commonly used to treat both hormone-producing (functional) and non-hormone-producing (nonfunctional) pituitary adenomas.
- Small to Medium-Sized Tumors: The endoscopic method is particularly effective for removing small to medium-sized pituitary tumors.
- Patients with Visual Disturbances: Surgery may be required in cases where the tumor exerts pressure on the optic nerves, causing visual impairments.
What Are the Risks of Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery carries certain risks:
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak (CSF Leak): During the surgery, a CSF leak may occur, which, although rare, can lead to meningitis (inflammation of the meninges).
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. However, minimally invasive techniques reduce the likelihood of infections.
- Nerve Damage: The optic nerves or other nearby nerves may be damaged during the procedure, potentially resulting in complications such as vision loss.
- Hormonal Imbalances: If the pituitary gland is damaged, hormonal imbalances may occur, necessitating long-term hormone replacement therapy.
Postoperative Recovery Process
The recovery process after endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is generally quicker and more comfortable compared to other surgical methods. Patients are typically monitored in the hospital for a few days following the surgery. Key points to consider during recovery include:
- Physical Activity: Patients should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous physical activities for the first few weeks after surgery. Light walking may be encouraged.
- Pain and Discomfort Management: Postoperative symptoms such as headaches or nasal congestion may occur but are usually mild and resolve within a few days.
- Hormone Tests: The hormone production capacity of the pituitary gland is monitored during the postoperative period. Blood tests are conducted to evaluate whether hormone levels are within normal ranges.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Postoperative follow-ups with the doctor are crucial to assess recovery progress and detect any potential complications early.
Success Rate of Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery
Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is a highly successful method for treating pituitary tumors. When performed by experienced surgeons, most pituitary tumors can be completely removed, significantly improving patients’ symptoms. The success rate of this method depends on factors such as tumor size, location, and the patient’s overall health. For hormone-producing pituitary adenomas, normalization of hormone levels is also a key success criterion.
Conclusion
Endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive option for treating pituitary tumors. This method helps patients recover more quickly, experience fewer complications, and return to their normal lives sooner. For patients diagnosed with pituitary tumors, this surgical approach offers highly satisfactory outcomes for both surgeons and patients. However, surgical decisions should always be made based on individual patient evaluations and recommendations from expert surgeons.