Baclofen and Spasticity Management
Spasticity is a condition characterized by abnormal muscle contractions and stiffness caused by damage to the central nervous system. It is a common complication of various neurological disorders such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injuries. Baclofen, a GABA-B agonist, works by inhibiting nerve signaling to promote muscle relaxation. However, oral baclofen therapy may be insufficient due to its limited penetration into the central nervous system and systemic side effects. In such cases, intrathecal drug delivery via a Baclofen pump provides higher efficacy by delivering the drug directly into the cerebrospinal fluid.
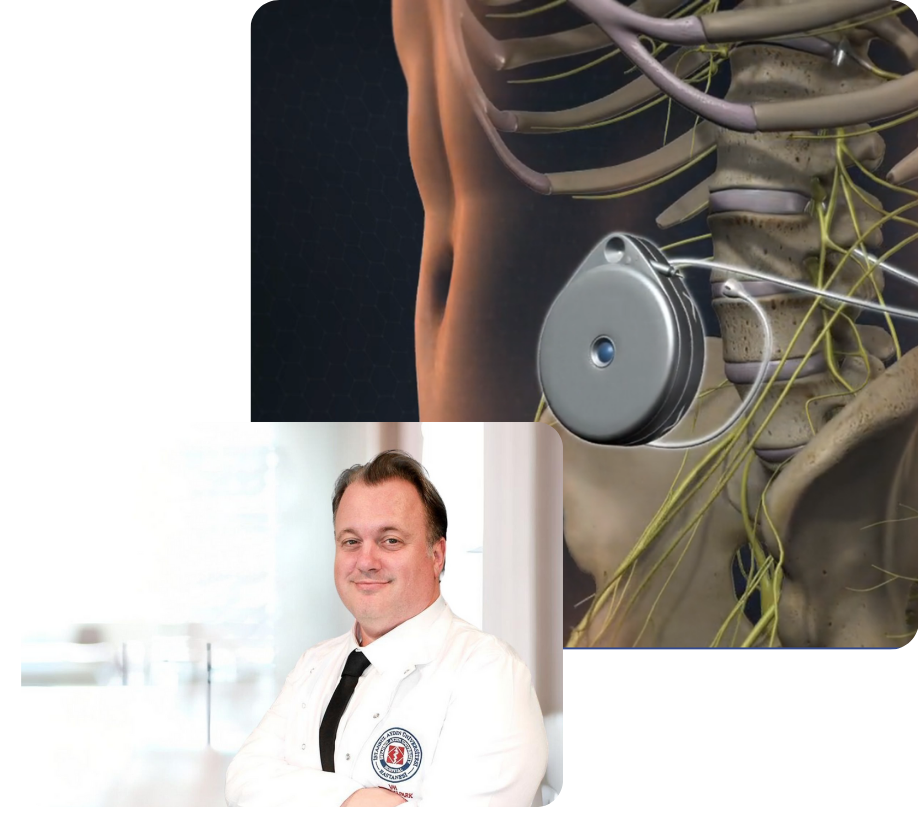
What Is a Baclofen Pump?
A Baclofen pump is a device used to control muscle tone by providing continuous baclofen infusion into the cerebrospinal fluid (intrathecal space). This implantable device is surgically placed in the abdominal area and delivers baclofen directly to the spinal cord via a catheter. It is especially ideal for patients resistant to oral therapy or those experiencing significant side effects.
The Baclofen pump consists of two main components:
- Pump (Medication Reservoir): The pump contains the medication reservoir and a microprocessor. It can be programmed to release the drug at specific intervals based on the patient’s treatment needs.
- Catheter: A thin tube that connects the pump to the spinal cord. The catheter delivers the medication directly into the intrathecal space.
Indications for Baclofen Pump
The Baclofen pump may be indicated in the following cases:
- 1. Severe Spasticity: Used in cases of severe spasticity, especially following cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and brain injuries.
- 2. Resistance to Oral Baclofen Therapy: If oral baclofen does not provide sufficient effect or causes side effects (e.g., sedation, muscle weakness, nausea) at high doses, a Baclofen pump may be preferred.
- 3. Focal Spasticity: For managing spasticity localized to specific muscle groups, a Baclofen pump offers a more targeted treatment approach.
- 4. Successful Trial Period: Before the surgical implantation of a Baclofen pump, a temporary intrathecal catheter is placed to evaluate the patient’s response to baclofen therapy. If successful results are obtained, permanent pump implantation is considered.
Baclofen Pump Implantation Process
The implantation of a Baclofen pump involves a careful, multi-step process:
1. Preoperative Evaluation:
- Patient Selection: The patient’s overall health, severity of spasticity, and response to baclofen therapy are assessed. Patient and family education is an essential part of the process.
- Trial Period: A temporary intrathecal catheter is used to deliver baclofen infusion. The patient’s response to this therapy and any potential side effects are observed. If spasticity is significantly reduced and side effects are manageable, permanent pump implantation is planned.
2. Surgical Procedure:
- Implantation of the Pump: Under general anesthesia, the Baclofen pump is surgically implanted in the abdominal region. The catheter is positioned to reach the cerebrospinal fluid within the spine.
- Programming: The pump is programmed according to the patient’s specific needs. Dosages and infusion rates are adjusted based on the patient’s spasticity level and response.
3. Postoperative Monitoring and Care:
- Regular Follow-Up: After pump implantation, patients are regularly monitored. The pump program is adjusted as needed, and the medication reservoir must be refilled at scheduled intervals.
- Side Effect Management: Patients must be closely monitored for potential side effects. Complications such as infections, catheter blockages, or medication overdose should be carefully managed.
Efficacy and Clinical Outcomes of Baclofen Pump
The efficacy of Baclofen pump therapy is closely tied to appropriate patient selection and proper surgical application. Clinical studies demonstrate that intrathecal Baclofen therapy is highly effective in reducing spasticity and improving patients' quality of life.
- • Reduction in Spasticity: The majority of patients report a significant decrease in spasticity with the Baclofen pump. This improvement enhances motor function and allows patients to perform daily activities more independently.
- • Pain Management: The Baclofen pump also alleviates pain associated with spasticity, reducing the need for pain-relieving medications.
- • Quality of Life: Controlling spasticity results in a marked improvement in patients’ overall quality of life. The Baclofen pump is particularly beneficial for patients with severe spasticity experiencing significant functional impairments.
Complications and Risks
Baclofen pump implantation is generally considered a safe procedure, but certain potential complications and risks exist. These risks can be minimized through careful surgical application and postoperative care.
1. Surgical Complications:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the site of the pump or catheter implantation. If symptoms of infection (e.g., pain, redness, swelling) appear, antibiotic treatment may be required.
- Catheter Blockage or Displacement: The catheter may become dislodged or blocked, impacting medication delivery. This issue may require surgical revision.
2. Medication-Related Complications:
- Baclofen Withdrawal: If the pump malfunctions or the catheter becomes blocked, Baclofen withdrawal may occur. This can lead to severe muscle spasms, fever, and seizures, requiring urgent intervention.
- Medication Overdose: An overdose of Baclofen can cause severe side effects, including respiratory depression, loss of consciousness, and coma. Proper programming and regular monitoring of the pump are essential to prevent this.
3. Sensory Disturbances and Paresthesia:
- The Baclofen pump may cause sensory changes, such as tingling or numbness, in some patients. These symptoms are typically temporary and can be alleviated by adjusting the pump settings.
Treatment Planning and Multidisciplinary Approach
Successful implementation of a Baclofen pump requires a multidisciplinary team approach. Neurologists, neurosurgeons, physical therapists, and nurses collaboratively manage the patient’s treatment process with precision.
1. Preoperative Evaluation:
- Patient selection is based on factors such as the severity of spasticity, response to oral therapy, and overall health status. Detailed information about Baclofen pump therapy must be provided to the patient and their family.
2. Surgical Planning:
- Careful surgical planning is essential to ensure proper placement of the pump and catheter. Surgical risks and potential complications should also be considered.
3. Postoperative Monitoring and Management:
- After pump implantation, patients must be regularly monitored. The pump program should be adjusted according to the patient’s needs, and refilling of the reservoir must be performed at scheduled intervals. Potential side effects and complications should also be closely observed.
Conclusion
The Baclofen pump offers an effective and safe treatment option for managing spasticity. For patients who do not respond to oral Baclofen therapy or experience severe side effects, intrathecal Baclofen therapy can provide significant improvements. Proper patient selection, meticulous surgical application, and rigorous postoperative management are key factors determining the success of this treatment method. The Baclofen pump significantly improves the quality of life and functional independence of patients suffering from spasticity. Therefore, Baclofen pump therapy is an advanced neuromodulation method that should be evaluated with a multidisciplinary approach for spasticity management.